Safety Light Curtain Working Principle Explained With Details
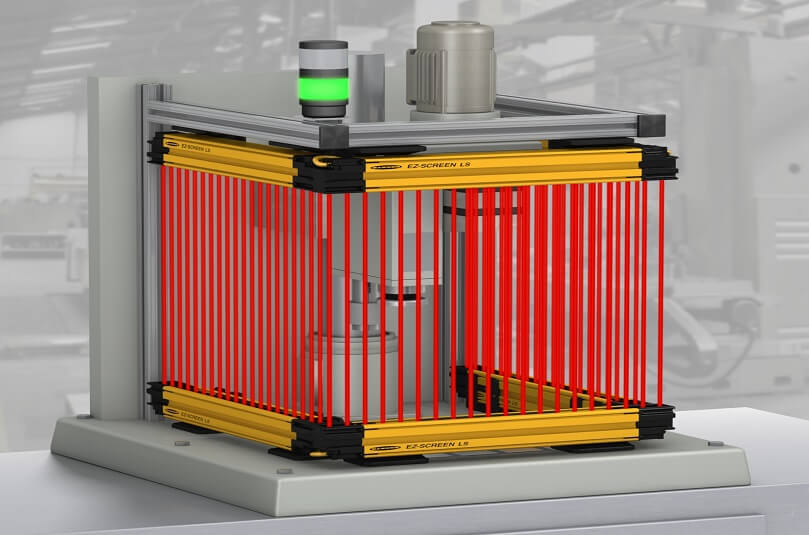
Safety light curtain is a crucial component in industrial and manufacturing environments providing a barrier between workers and dangerous machinery. This device uses infrared or laser beams to detect any movement or obstruction within a specific area, instantly shutting down the machine if a potential hazard is detected. This article will delve into the safety light curtain working principle explaining how it keeps workers safe and why it is becoming an increasingly popular solution in the industry.
What is a Safety Light Curtain?
A safety light curtain is used to safeguard access areas, danger points or danger zones. It is designed for accident prevention following applicable international standards. The safety light curtain consists of a transmitter and a receiver which are optically synchronized.
The infrared beams are controlled and monitored via a microprocessor. As soon as at least one of the beams emitted by the transmitter is interrupted, the light curtain outputs switch to low and the hazardous movement is stopped.
In machine safety applications you can see different kinds of safety devices. A safety light curtain is one of the most unique solutions for safety applications such as:
- Automatic machinery.
- Packaging, handling and storage machinery.
- Textile processing, woodworking and ceramic processing machinery.
- Automatic or semi-automatic assembly lines.
- Automated high-bay racking.

Safety Light Curtain Working Principle
A light curtain comprises two units, namely a transmitter and a receiver between which coded infrared beams are sequentially exchanged. The protective field is the area enclosed by these two components, the emitted light beams forming a permanent, though invisible, shield between the two units. The receiver unit is connected to a safety relay. The safety relay transmits the signal to the machine control unit.

Synchronization between the sender and receiver devices is performed optically, i.e. wired connection between the two units is not necessary. When properly installed, the protective device detects any relevant entry into the hazardous area. As soon as such an entry is detected, the protective device immediately triggers the safety relay, which in turn causes the machine control system to bring the machine to a safe status and/or complete stop, thus eliminating the hazard. Any internal fault is detected by the device’s permanent self-control function and has the same result as an intrusion into the protective field.
The size of the protective field depends on the dimension of the active optoelectronic protective device and the distance between the sender and receiver units. Active optoelectronic protective devices are also commonly used as sensors to automate industrial operations where no critical human safety issue is involved. However, when directly linked to the safety of persons, their design and installation are strictly regulated.
The unique operating principle of this device presents several advantages over mechanical safeguarding devices.
- Access time to the machine is reduced, thereby increasing productivity.
- Workplace ergonomics are greatly improved and less space is required.
- The invisible infrared beams allow better visibility of the machine and operating process.
- Protection applies to an approaching person.
1-Finger and hand detection
Detects a human finger when workers operate very close to the hazardous point of the machine.

2-Hand and person detection
Detects hands and prevents start-up while a person is in a hazardous area.

3-Single-sided access protection
Approaching persons are detected by identifying a person’s body.

4-Multi-sided access protection
Approaching persons are detected by identifying a person’s body.

5-With differentiation between person and material
Approaching persons are detected by identifying a human body. A distinction is made between humans and materials.

6-Person detection
Approaching and present persons are detected by identifying legs in the scanning range.

Positioning the safety light curtains
The level of safety depends on the way the device is positioned. The risk assessment conclusions will help decide what position is best suited for preventing foreseeable hazards. To ensure proper safeguarding, special care must be taken to find a position that will not allow the protective device to be bypassed and such that any hazardous machine movement is safely stopped before potential harm occurs.
There are different classical ways to position safety light curtains:
– Vertically (“perpendicular approach”)
– Horizontally (“parallel approach”)
– In an L shape (vertically and horizontally combined)
– Inclined (“angular approach”).
It must not be possible to pass over, below, around or go behind the protective field. When positioning light curtains it must not be possible to pass over the highest beam, below the lowest beam or between two beams. If this cannot be guaranteed, then additional protective devices must be used.



 Types of Timer Relays and Their Applications
Types of Timer Relays and Their Applications  Relay Applications: Real-Life And Industrial Examples
Relay Applications: Real-Life And Industrial Examples  Types of Micro Switches and Their Applications
Types of Micro Switches and Their Applications  Best Voltage Testers for Home Use: 2023 Edition
Best Voltage Testers for Home Use: 2023 Edition  Advantages of Transducers for Optimal Measurement
Advantages of Transducers for Optimal Measurement  Advantages of Infrared Sensors: Improved Accuracy and More
Advantages of Infrared Sensors: Improved Accuracy and More